IGD recently provided detectably better N₂O gas detectors to the NHS. Issues of high-level N₂O leakage across the service led to concern among safety management, especially due to its prevalence across the NHS. They were looking for a reliable and high-quality N₂O gas detector solution to prevent this exposure and found that IGD was best suited to provide this solution. Read below to find out more about this project.
You can download a PDF version of this case study here.
Where is N₂O Used in the NHS?
N₂O (or Entonox) is used widely across the NHS, being a part of everyday surgeries and medical procedures across almost all medical departments, especially maternity wards, birthing suites and dental practices. Commonly administrated as a mixture of 50% air and 50% N₂O. It provides a euphoric and anaesthetic effect by inhibiting nerve cells and preventing pain. Coupled with its ability to be used safely, makes it an effective gas for use in medical facilities. Due to its widespread usage, it is often stored in large quantities within these applications and has heavy usage, requiring N₂O gas detectors.
How is N2O Dangerous? and What are the Limits of Exposure?
N₂O may not be perceived as dangerous because of how frequently it is used. However, N₂O has regulated workplace exposure levels. In the UK, the UK Health and Safety Executive, under COSHH, outlines that no person should be exposed to 100ppm or more of N2O over an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA).
In the USA, OSHA has much lower exposure levels at 25 ppm over an 8-hour time-weighted average. With no Short-Term Exposure, it makes N2O a highly dangerous substance if an uncontrollable leak occurs. N₂O can cause short-term issues with mental performance, audiovisual ability, and manual dexterity.
Long-term exposure can also cause vitamin B12 deficiency, numbness, and reproductive side effects. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (USA) recommends that “workers’ exposure to N₂O should be controlled during the administration of anaesthetic gas in medical, dental, and veterinary operators.”
Workers’ exposure to N₂O should be controlled and mitigated as much as possible. Those at risk of N₂O are personnel who frequently administer or utilize the gas as part of their daily work routine. This includes midwives, nurses, dentists, veterinarians, researchers, and bottle-filling personnel.
It is also worth mentioning that N₂O is a damaging greenhouse gas, with a Global warming potential of 310 times the impact of Carbon Dioxide. This means even small leaks can have a long-lasting impact on both the health of personnel and the environment.
What were the Concerns of the NHS?
The exposure limit is very low for N₂O; thus, uncontrolled leaks can happen easily. In addition, nurses and midwives are potentially exposed to background levels of N2O on maternity wards, where patients use Entonox. The major concern for the NHS was the long-term exposure of their staff on the wards and if leaks were to go unnoticed. This was a major concern for the NHS, to detect leaks and ensure that nurses don’t breach the TWA threshold while working. Continuous monitoring was need in the wards for leak detection; as well as the ability to monitor individual nurses’ exposure levels to ensure nurses and midwives did not breach the legislated occupational exposure levels.
IGD’s Detectably Better Solution for the NHS
The NHS required a fixed and portable monitor solution that could detect low-level leaks and reliably measure nurses’ Time Weighted Average exposure. They chose IGD’s N₂O gas detector solution, consisting of the TOC-750S sampling gas detector and the mPower POLI portable, which is ideal for the medical industry due to its wide range of features and benefits.
The TOC-750S is a sampling N₂O gas detector that provides high-quality gas detection in areas that are difficult to reach or harsh for normal diffusion sensors, such as those used in our TOC-750 Safe Area detector. Almost silent in operation and featuring virtually no moving parts, the 750S is easy to clean and operate. The system provides real-time digital readings and event logs that health and safety personnel can download straight to a phone or laptop.
Providing a 1ppm resolution and extreme zero stability for N₂O detection, which ensures gas is detected before it becomes hazardous to health. It is a unique solution designed and manufactured by IGD in the UK and is currently the world’s only low-level, stable, fixed N₂O detector.
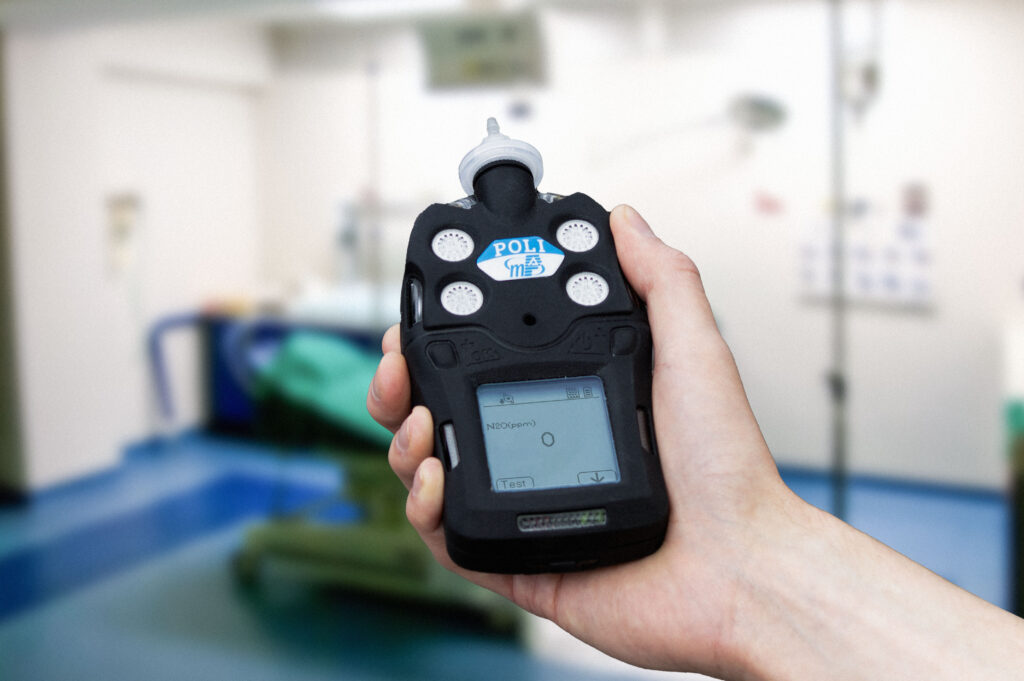

The POLI N2O gas detector is a fully customizable multi-gas detector that is perfect for the medical industry. It is small, lightweight, and durable, making it easy for personnel to perform effective detection without being held back by a weighty device. It measures individual exposure levels and will automatically calculate the 8-hour time-weighted average.
Featuring audible, visual, and vibration alarms that personnel can use to instantly know when they have breached the 8-hour exposure level. The POLI is USB rechargeable and does not require any bulky cradles or software. The easy-to-use interface on both the POLI and PC software means training and adoption into safe operating procedures is seamless.
The combined approach of using fixed and portables means the NHS has 24/7 coverage for N₂O leaks, and nurses can monitor their personal TWA using a POLI. The NHS received the solution, servicing, and support from IGD.
IGD provide free owner-operator training to ensure site-designated personnel know how to use the portables and incorporate the combined solution into safe operating procedures. Overall, the solution was a breakthrough for the NHS, enhancing their safety throughout their sites and maternity wards.
Contact IGD today to learn more about our detectably better N₂O gas detector solutions or for over 700 gases and vapours. Backed by over 100 years of gas detection experience. Check out the TOC-750S sampling gas detector and mPower POLI Multi-Gas product pages for more information.



